Being proficient with prompt engineering basics has become an essential skill nowadays. Many of us talk to AI almost daily. Sometimes, it’s even without our knowledge as the number of voice chatbots increases. However, today, we’ll talk specifically about how to talk to generative AI.
Generative AI prompt engineering can be a bit tricky because you aren’t just ‘venting’ to a machine or going through some customer service routines. The goal here is to word your command in such a way that you get the most accurate result. You can use the knowledge of AI prompt engineering to complete a great variety of tasks, from generating an image to developing and programming an AI voice bot.
Moreover, all of these tasks are becoming more relevant with every passing day. According to the CompTIA IT Industry Outlook 2024 report, 22% of companies insist on AI integration in the workflow. The percentage of using AI in daily work by usual employees is even higher. However, only a few know how to interact with AI most efficiently.
Our highly qualified specialists maintain that prompt engineering is the main thing that most GenAI users need to improve. So, with their help, you’ll be able to learn the basics of prompt engineering.
Prompt Engineering Basics: What Is Prompt Engineering?
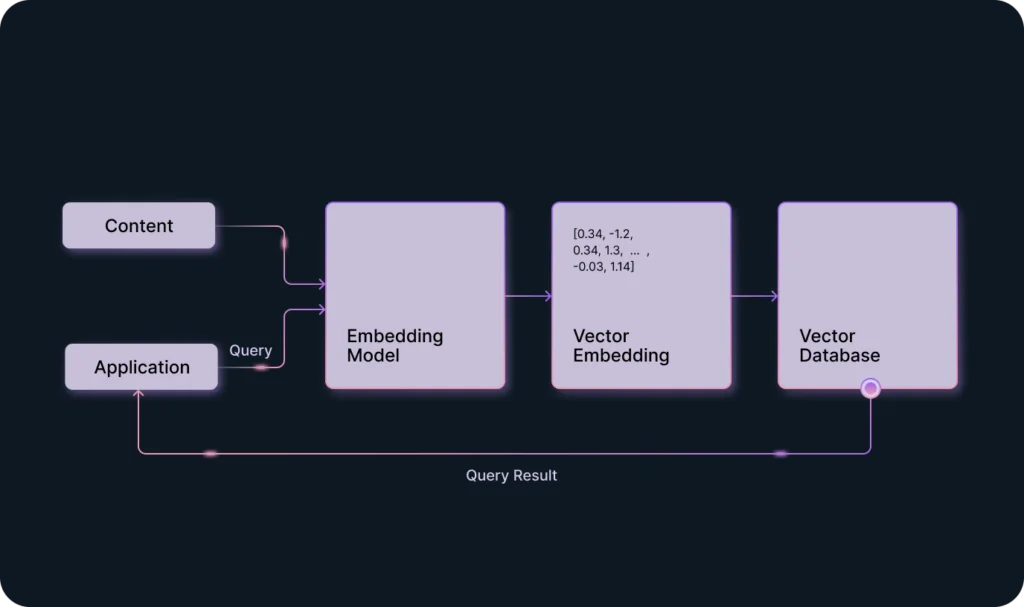
Prompt engineering is creating inputs as specific instructions for large language models (LLMs, more on that here).
Generative AI models generate specific outputs based on the quality of provided inputs. We call these inputs prompts, and the practice of writing them is called prompt engineering.
Prompt engineering helps LLMs better process the incoming tasks to produce desired outputs.
Where You Can Apply Prompt Engineering Basics
AI software development
Prompt engineering now plays an active role in software development. You can save a great deal of time time by giving the AI model a clear prompt describing the desired functionality. It suggests code snippets or even complete entire functions. That is very helpful, especially for repetitive tasks. Trained on developer prompts, AI can also analyze existing code and identify potential bugs. If you want to read the opinion of Devtorium`s developers on AI code generation tools, check out this post.
Chatbot development
Prompt engineering allows chatbots to respond more naturally and informatively. You provide them with clear instructions and context for understanding customer inquiries. A better understanding of customer questions leads to improved chatbot responses, which means happier customers and shorter wait times. If you want to create your chatbot, read our blog about Assistant API.
Cybersecurity services
Cybersecurity is another field where understanding prompt engineering basics can help you. Security analysts can leverage prompt engineering to guide AI systems in analyzing network activity and logs. AI can efficiently scan vast amounts of data and flag potential security threats when given prompts with specific indicators of compromise (IOCs) or suspicious behavior patterns. Prompt engineering in cybersecurity empowers security professionals by harnessing AI’s analytical power to identify threats, uncover vulnerabilities, and respond to incidents.
Creative content generation
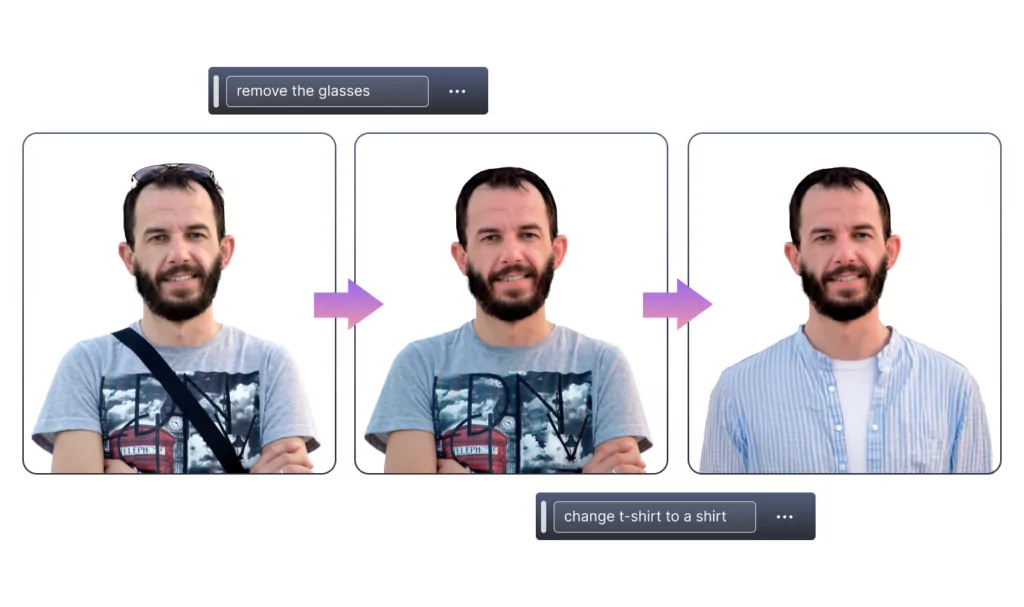
Prompt engineering allows writers to enhance their efficiency. You can give an AI model a starting point and direction for generating creative text formats like blogs, posts, scripts, or even musical pieces. This frees up the writer to focus on refining and polishing the ideas. The same goes for any kind of content, be it visuals, text, or even music.
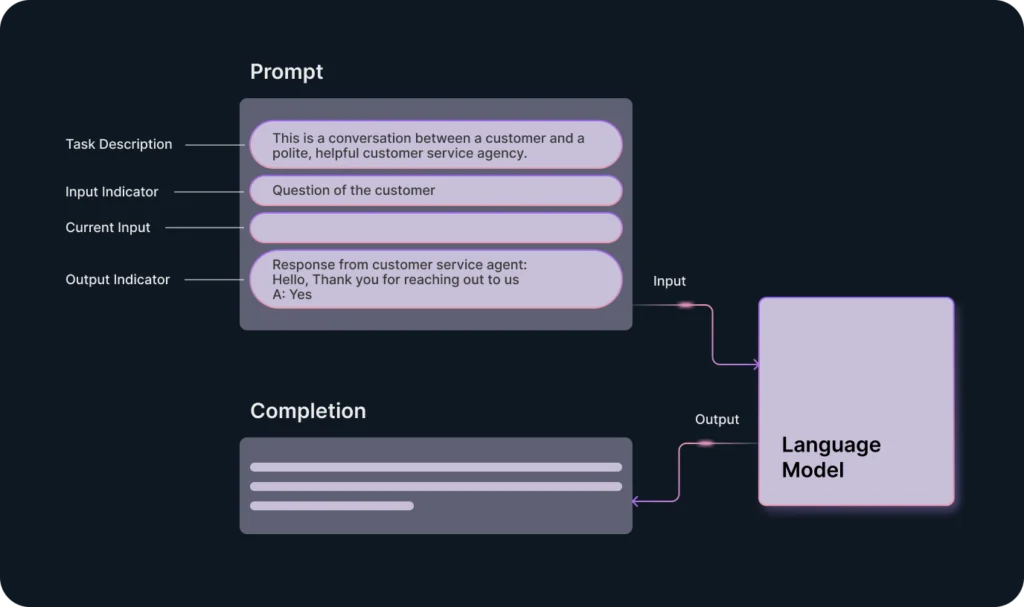
Essential Tips on Prompt Engineering Basics
Prompt engineers do not only design and develop prompts. They also operate a wide range of skills and techniques that improve the interaction and development of LLMs. Their work encompasses the following:
- Zero-shot prompting – instructing LLM without relying on any examples.
- Few-shot prompting – giving the model a few examples before instructing.
- Chain-of-thought prompting (CoT) – asking the model to explain its steps every time it performs the instruction.
Here are a few tips that will help you communicate with an AI as a prompt engineer on the basic level:
- Use clear instructions and ask direct questions. Make the sentences as concise as possible.
- Provide LLM with context. Use any relevant data for it.
- Give examples in prompts.
- Specify the desired output format and length.
- Align prompt instructions with the task’s end goal.
- Provide the desired output with styles such as bullet points, tables, numbered lists, inline/block code, quotes, hyperlinks, etc.
- Let the LLM answer “I don`t know” if needed.
- Break the complex tasks into subtasks.
- Use a clear separator like “###” to split the instruction and context.
- Experiment a lot to see what prompts work best.
Bottom Line: Are Prompt Engineering Basics Enough to Talk to an AI?
So, to sum up, everyone who uses GenAI can learn the easiest prompts to get desired but simple outputs. However, to get more complex results, you will need to have a really good understanding of programming and mathematics. Therefore, if you need to use AI in your project as more than a simple user, contact our team for a free consultation on how to best implement its power for you!